
Alberta Environment and Parks, Canada
From 2016 – To 2017
Model, report, and training delivered for use in management scenario evaluation.

President and Senior Consultant
pmcraig@dsi.llc

Chief Engineer
ntlam@dsi.llc

Hydrologist
bmhoa@dsi.llc
Alberta Environment and Parks (AEP) has developed a South Saskatchewan Region Plan (SSRP) to flexibly and proactively manage the cumulative effects of human activity on surface water quality within the South Saskatchewan Region. Scientific models used to evaluate the effectiveness of various management and engineering environmental options have been a key component of the management approach. As part of SSRP, AEP commissioned an in-stream water quality model for the Little Bow River.
The Little Bow River watershed is located in the headwaters of the Oldman River Basin in the southern region of the Province of Alberta. As a major tributary of the Oldman River, the Little Bow River receives diverted flows from the Highwood River, direct precipitation, local runoff, and municipal/industrial discharges. The Upper Little Bow River Basin occupies an area of approximately 3,491 km$^2$, and supports a wide variety of natural resources, including forests, minerals, wildlife, and agricultural lands.
The project goal was to develop a hydrodynamic and water quality model of the Little Bow River as an assessment tool to support flood mitigation work related to the Highwood-Little Bow diversion system and Little Bow River.
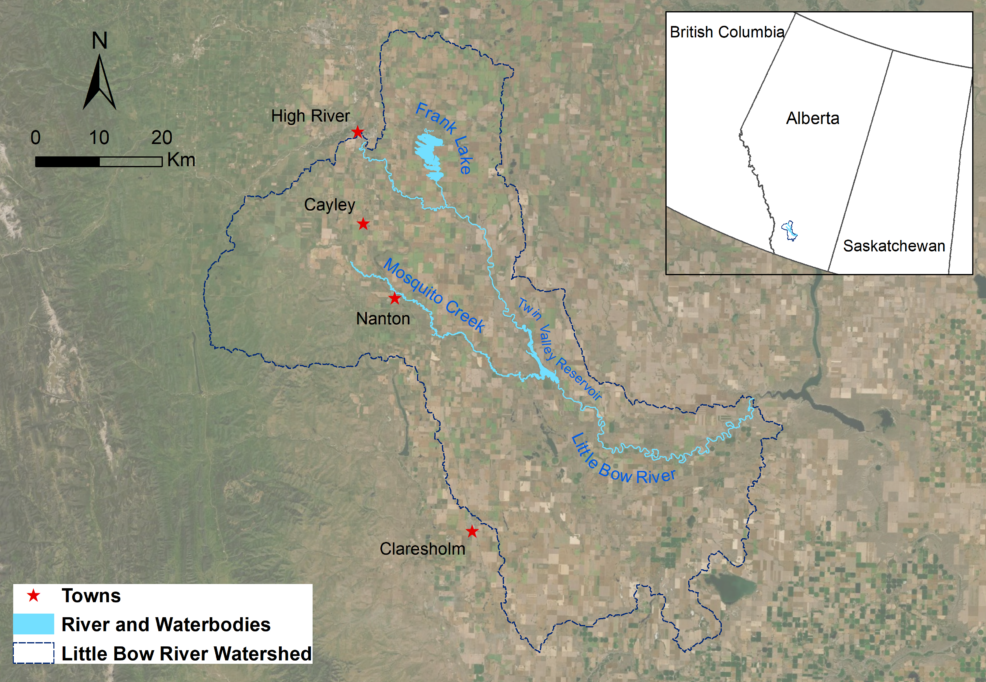
Using Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code Plus (EFDC+), DSI developed a two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) model of the Little Bow River, which extended about 165 km and included an in-stream reservoir (Twin Valley), and a 55 km tributary (Mosquito Creek). The reaches were represented by 2D grids and the reservoir was represented using 3D grids. The model boundary condition inputs were provided using monitoring data and a watershed model developed using Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT).
The model simulated hydrodynamics, temperature, ice, dissolved oxygen, nutrients, macrophytes, algae, and the processes involved in the complete nutrient cycle. Following the calibration of the model for all physical, chemical, and biological parameters, DSI used the calibrated model of the complete system to evaluate multiple management scenarios, including flow diversion at Highwood, reservoir operations, and Waste Water Treatment Plant (WWTP) effluent water quality control.
DSI submitted the complete model and the final report to AEP and provided training to agency staff. AEP uses the model for management scenario evaluation.This video demonstrates how the Little Bow River WQ simulation helps better understand and manage water resources.